Peter Thiel was the cofounder of Paypal and Palantir Technologies and was also the first outside investor in Facebook. This book is his philosophy on how startups and small businesses must go from zero to one to be dominant in the marketplace.
Every moment in business happens only once. The next Bill Gates won’t make an operating system. The next Mark Zuckerberg won’t create a social network. If you’re copying them you’re not doing anything different, you’re merely going from 1 to n.
There is no science with business. How do you get from zero to one? Should be your chief priority if you’re a founder or entrepreneur.
Zero To One
For a startup or business to stick and survive in the long run, it must be a monopoly. How do you go from Zero to One? The biggest leaps in progress are vertical and not horizontal.
Zero To One is the future of progress. If you take one typewriter and build 100, you have made horizontal progress. If you have a typewriter and build a word processor, you have made vertical progress.
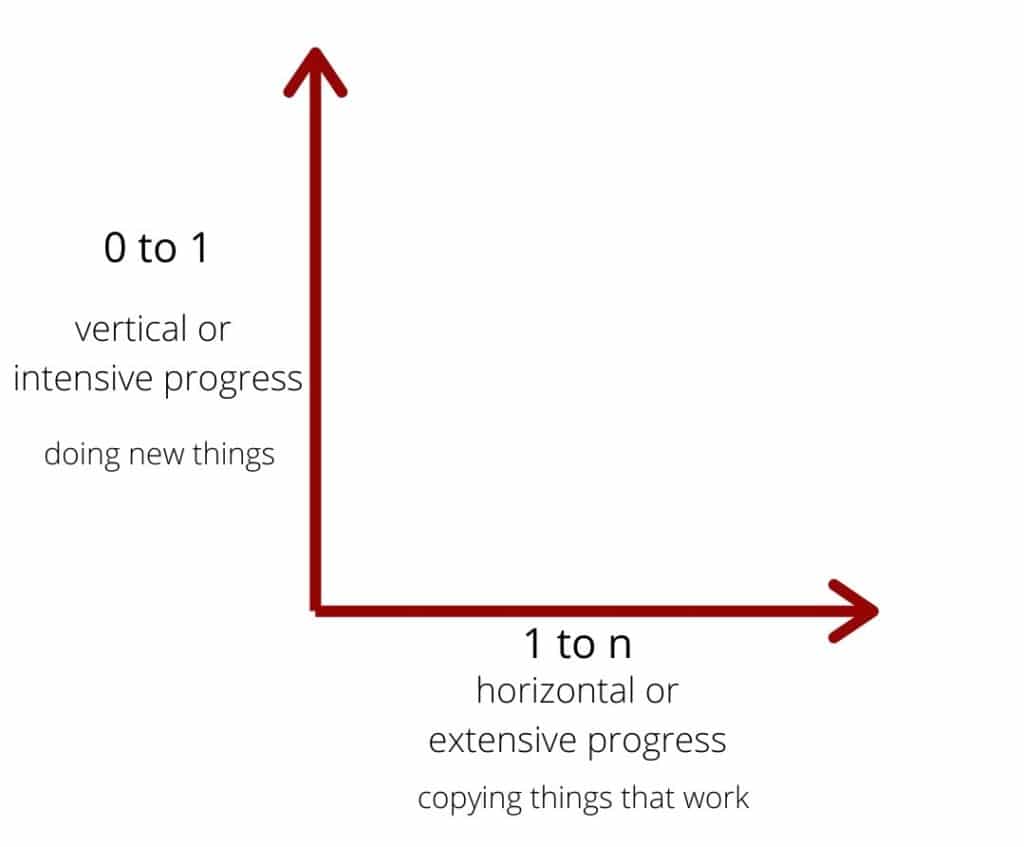
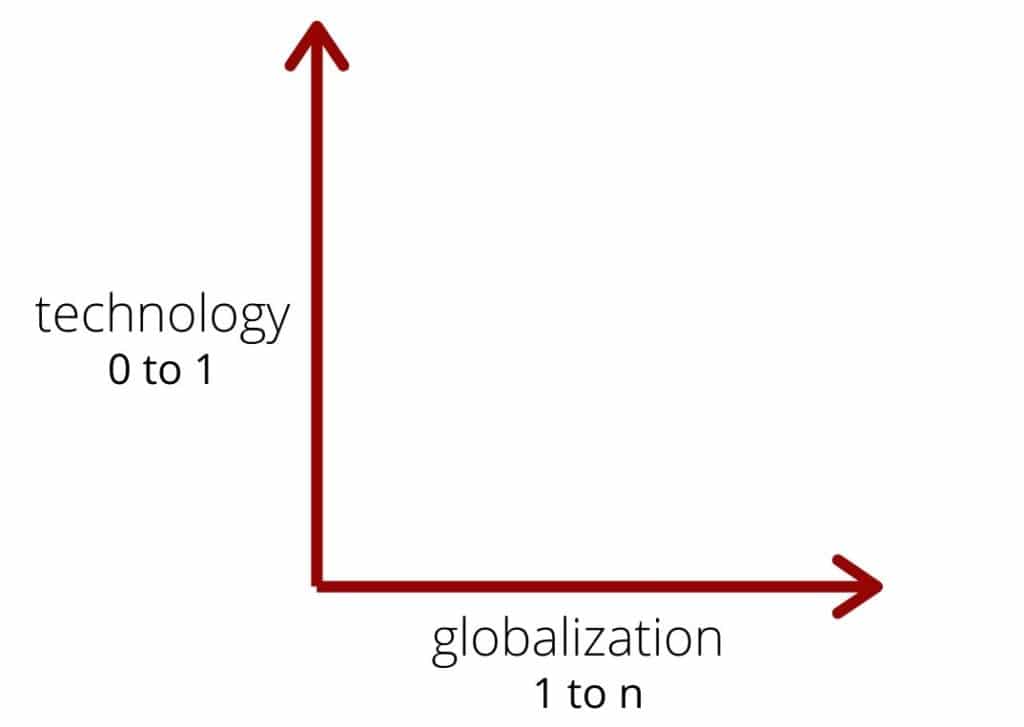
Globalization is taking things that work and making them everywhere. It is an example of 1 to n. We have a model and we copy it there is no innovation here. Technology on the other hand is 0 to 1.
A startup is a group of people on a mission who think of a different future. They hold a contrarian truth. It may even sound delusional since most people think the answer to be x in fact it’s the opposite of x.
Monopoly
For a startup to have massive success, it must be a monopoly in its market. You must be so good at what you offer that competitors don’t stand a chance. Peter Thiel recommends be 10x your competitors.
Bet your business on a contrarian truth. All failed companies have one thing in common: they failed to escape competition. A monopoly isn’t worth much unless it is protected.
A monopoly owns its market, so it can set its own prices. Since it has no competition, it produces at the quantity and price combination that maximizes its
profits.
People who have monopolies don’t talk about it to avoid being audited and scrutinized, and people who don’t do to boast their products and services as the next big thing. Monopoly is the condition of every successful business.
Network Effects
It’s important to dominate a niche market and then scale up for the business to endure the long run. The Market knows far more than you ever could.
All leading businesses initially tested the waters and then went ahead to introducing it to all segments of society and not the other way around as we see it happening to budding startups today.
Facebook was initially used in college campuses and later caught on. Paypal initially paid people to sign up and gave bonuses to those who referred. They started testing their product on eBay and now it’s widely used all over the world. Jeff Bezos started with selling books now amazon sells any and everything.
Don’t have a bleak view of the future. It might seem like we have already discovered everything, but there are many secrets left to be discovered. Invent something completely remarkable.
After the testing phase, ensure the customer’s lifetime value exceeds the customers acquisition value that’s the total net profit earned per customer.
The Seven Big Questions
The following are the seven big questions: every startup or business must ask themselves if you don’t have the answers to 4 or 5 don’t even start.
A startup messed up at its foundation cannot be fixed.
Peter Thiel
- The Engineering Question
Can you create breakthrough technology instead of incremental improvements? - The Timing Question
Is now the right time to start your particular business? - The Monopoly Question
Are you starting with a big share of a small market? - The People Question
Do you have the right team? - The Distribution Question
Do you have a way to not just create but deliver your product? - The Durability Question
Will your market position be defensible 10 and 20 years into the future? - The Secret Question
Have you identified a unique opportunity that others don’t see?
The best way to go from 0 to 1 is to create new things for the future that will not just make it different, but better.







3 thoughts on “Zero To One by Peter Thiel – Summary”
Great summary indeed.
Thanks Lethu I appreciate it.
Love it! Keep it up!